How to protect switches against rogue DHCP servers?
 Zyxel Employee
Zyxel Employee



This example will instruct the administrator on how to configure the switch to protect the network from attackers sending false IP configurations to clients. DHCP Snooping blocks DHCP offers coming from an untrusted port. Untrusted ports are usually ports connected to office workstations or publicly accessible jacks.
Note:
All network IP addresses and subnet masks are used as examples in this article. Please replace them with your actual network IP addresses and subnet masks. All UI displayed in this article are taken from the XGS4600 series switch.
1. Configuration in the Switch
1-1. Access the Switch’s Web GUI.
1-2. Go to Advance Application > VLAN > VLAN Configuration > Static VLAN Setup. For this example, all traffic entering access ports are sent to VLAN 1. VLAN 1 should be fixed and untagged for all access ports. Click Add.
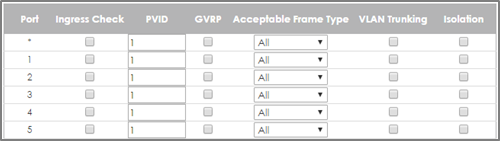
1-3. Go to Advance Application > VLAN > VLAN Configuration > VLAN Port Setup. Configure all access ports with PVID 1. Click Apply.
1-4. Go to Advance Application > IP Source Guard > IPv4 Source Guard Setup > DHCP Snooping > Configure. Check the Active box under DHCP Snooping Configure. Click Apply.
1-5. Go to Advance Application > IP Source Guard > IPv4 Source Guard Setup > DHCP Snooping > Configure > Port. Set all access ports as untrusted ports. Ports to the USG or other network components should be trusted ports. Click Apply.
1-6. Go to Advance Application > IP Source Guard > IPv4 Source Guard Setup > DHCP Snooping > Configure > VLAN. Input the Start VID and End VID. Make sure that the PVID of the access ports are included in this range. Click Apply.
1-7. After inputting the VID range, a list of VID should appear below. Select Yes for the access ports’ VLANs. Click Apply.
2. Test the Result
2-1. Connect the Rogue-DHCP on one of the access ports. Create the following DHCP Pool on the LAN interface:
Starting IP Address: 172.16.1.10
End IP Address: 172.16.1.20
2-2. Connect DHCP clients on the other access ports. The clients should only be receiving IP Addresses provided by the USG.
3. What Could Go Wrong
3-1. If the DHCP clients in the publicly accessible ports are using IP Addresses provided by the Rogue-DHCP:
3-1-1. Make sure that all ports connected to publicly accessible ports are an untrusted port in Advance Application > IP Source Guard > IPv4 Source Guard Setup > DHCP Snooping > Configure > Port.
3-1-2. Verify the PVID of the port to this DHCP client. Make sure that DHCP snooping is enabled for that VLAN in Advance Application > IP Source Guard > IPv4 Source Guard Setup > DHCP Snooping > Configure > VLAN.
3-2. If the DHCP clients in the publicly accessible ports are not able to receive IP Addresses provided by the real DHCP server:
3-2-1. Make sure that the port to the real DHCP is a trust port in Advance Application > IP Source Guard > IPv4 Source Guard Setup > DHCP Snooping > Configure > Port.
3-2-2. Make sure that both redundant ports are trusted ports in Advance Application > IP Source Guard > IPv4 Source Guard Setup > DHCP Snooping > Configure > Port when using a ring topology.
Categories
- All Categories
- 442 Beta Program
- 2.9K Nebula
- 220 Nebula Ideas
- 127 Nebula Status and Incidents
- 6.5K Security
- 602 USG FLEX H Series
- 344 Security Ideas
- 1.7K Switch
- 84 Switch Ideas
- 1.4K Wireless
- 52 Wireless Ideas
- 7K Consumer Product
- 298 Service & License
- 481 News and Release
- 92 Security Advisories
- 31 Education Center
- 10 [Campaign] Zyxel Network Detective
- 4.8K FAQ
- 34 Documents
- 87 About Community
- 105 Security Highlight