How to configure the switch to separate VOIP traffic from data traffic
 Zyxel Employee
Zyxel Employee



The example shows administrators how to use Voice VLAN to separate untagged VOIP traffic from untagged data traffic. Unlike traditional VOIP applications, the Voice VLAN feature separates VOIP and data traffic as traffic reaches the switch. This means that the VLAN architecture begins on the switch and not on the IP Phones themselves.
Note:
All network IP addresses and subnet masks are used as examples in this article. Please replace them with your actual network IP addresses and subnet masks. This example was tested using XGS4600-32.
1. Configure VLAN 100 for IP phone
1-1. Configure VLAN 100 on Switch. VLAN 100 is created as the Voice VLAN for the IP Phone.
2. Configure Voice VLAN
2-1. Enter the web GUI and go to: Menu > Advanced Application > VLAN > VLAN Configuration > Voice VLAN Setup. Input the Voice VLAN. In this example, it is VLAN 100. Click “Apply”.
2-2. Configure the OUI Setup: Enter the web GUI and go to: Menu > Advanced Application > VLAN > VLAN Configuration > Voice VLAN Setup. Set the OUI address. (You can key in the MAC address.) In this example, it is cc:5d:4e:64:de:77. Set up the OUI mask as ff:ff:ff:00:00:00. Click “Add”.
Note:
This will instruct the switch to process any traffic from devices with MAC address between cc:5d:4e:00:00:00 and cc:5d:4e:ff:ff:ff into the Voice VLAN.
3. Test the Result
3-1. Go to Menu > Management > MAC Table > Search. Check the MAC address table. The IP Phone is assigned to VLAN 100.
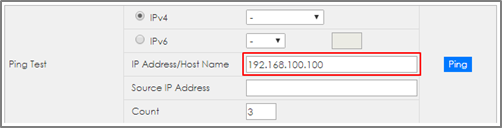
3-2. Enter web GUI and go to Menu > Management > Diagnostic > Ping test. Use Switch to ping IP Phone. Switch can ping IP Phone successfully.
4. What Could Go Wrong
4-1. If the IP phone is not assigned to the voice VLAN, please verify the MAC address of the IP phone. The MAC address can usually be found on the label or sticker underneath the IP phones. This MAC address must be within the range of the Voice VLAN OUI settings.
4-2. Here are the expected behaviors of IP phones based on the different settings. If you find the behaviors of the IP Phone is not the same as your expectation, please refer below:
4-2-1. If the IP Phone is VLAN enabled and this VLAN is the same as Voice VLAN: The Switch will keep the Voice VLAN and assign the priority setting to the IP phone. The IP phone will only recognize the tagged traffic. In this case, port 1 in VLAN 100 on Switch should be set as tagged out (check the TX tagging box).
4-2-2. If the IP Phone is VLAN enabled and this VLAN is different from the switch’s Voice VLAN: The Switch will not apply any changes on the VOIP traffic of the IP Phone.
4-2-3. If the IP Phone is VLAN disabled: The Switch will assign the Voice VLAN and priority setting to the IP phone’s VOIP traffic. This setting causes the IP Phone to only send and receive untagged traffic. In this case, port 1 in VLAN 100 on Switch should be set as untagged out (uncheck the TX tagging box).
Categories
- All Categories
- 442 Beta Program
- 2.9K Nebula
- 219 Nebula Ideas
- 127 Nebula Status and Incidents
- 6.5K Security
- 603 USG FLEX H Series
- 344 Security Ideas
- 1.7K Switch
- 84 Switch Ideas
- 1.4K Wireless
- 52 Wireless Ideas
- 7K Consumer Product
- 298 Service & License
- 481 News and Release
- 92 Security Advisories
- 31 Education Center
- 10 [Campaign] Zyxel Network Detective
- 4.8K FAQ
- 34 Documents
- 87 About Community
- 105 Security Highlight